If you’re running a Rockit Server onboard (quietly humming away in the nav station), the OpenCPN Chart Plotter makes a brilliant “situational awareness” layer on top of your performance data collection stack.
This guide walk you through a clean install of OpenCPN on a Rockit Server Device.

What you’ll need
- Rockit Server running Raspberry Pi OS (Bookworm, 64‑bit).
- Internet access with the Rockit Server online via Wi-Fi.
- The default rockit user has sudo access out of the box when the server boots so you have admin rights to install additional software.
- (Optional) Your chart sets — download from an online source (e.g., o‑charts) to local storage on the Rockit Server (e.g., ~/Charts).
Tip: If you’re using our standard Rockit Server image, you can log in with from Windows PC/IPAD/Apple Mac using VNC Viewer.
Step 1 — Update the system
Open a terminal session and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt full-upgrade -y sudo reboot
This will update the software installed on the Rockit Server device.
Both Terminal and LXTerminal are preinstalled on the Rockit Server device and can be found on the Utilities or System Tools menus.
Step 2 — Install OpenCPN
This guide uses Flatpak to install the OpenCPN software. Flatpak is a software management application for the Linux operating system that is the base operating system for the Rockit Server device. Flatpak will deliver the latest stable OpenCPN build minimising the amount of work that you have to do to find the correct version.
1) Install Flatpak (if not already):
sudo apt install -y flatpak
2) Enable Flathub:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
3) Install OpenCPN:
sudo flatpak install -y flathub org.opencpn.OpenCPN
4) Launch it (from the desktop menu or):
flatpak run org.opencpn.OpenCPN
Step 4 — First‑run wizard & basic settings
When OpenCPN starts the first time:
- Units & UI: set NM/knots/° and a sensible UI scale for the Rockit Server screen or your remote desktop.
- Charts Directory: after downloading, add your local charts folder (e.g. ~/Charts).
- GPS: Skip for now—we’ll bind data sources next.
Step 5 — Connect OpenCPN to your live data
Rockit Servers provide different data paths depending on the model.
- Rockit Server Model 1: This device doesn’t have a direct N2K port so use Wi‑Fi to join an onboard NMEA‑0183 multiplexer or an N2K→Wi‑Fi/TCP gateway.
- Rockit Server Model 3: built‑in NMEA 2000 backbone connection via the onboard CAN interface (SocketCAN). The interface appears as can0. OpenCPN can read N2K directly from can0. If you prefer network feeds, use NMEA‑0183 over Wi-Fi TCP/UDP.
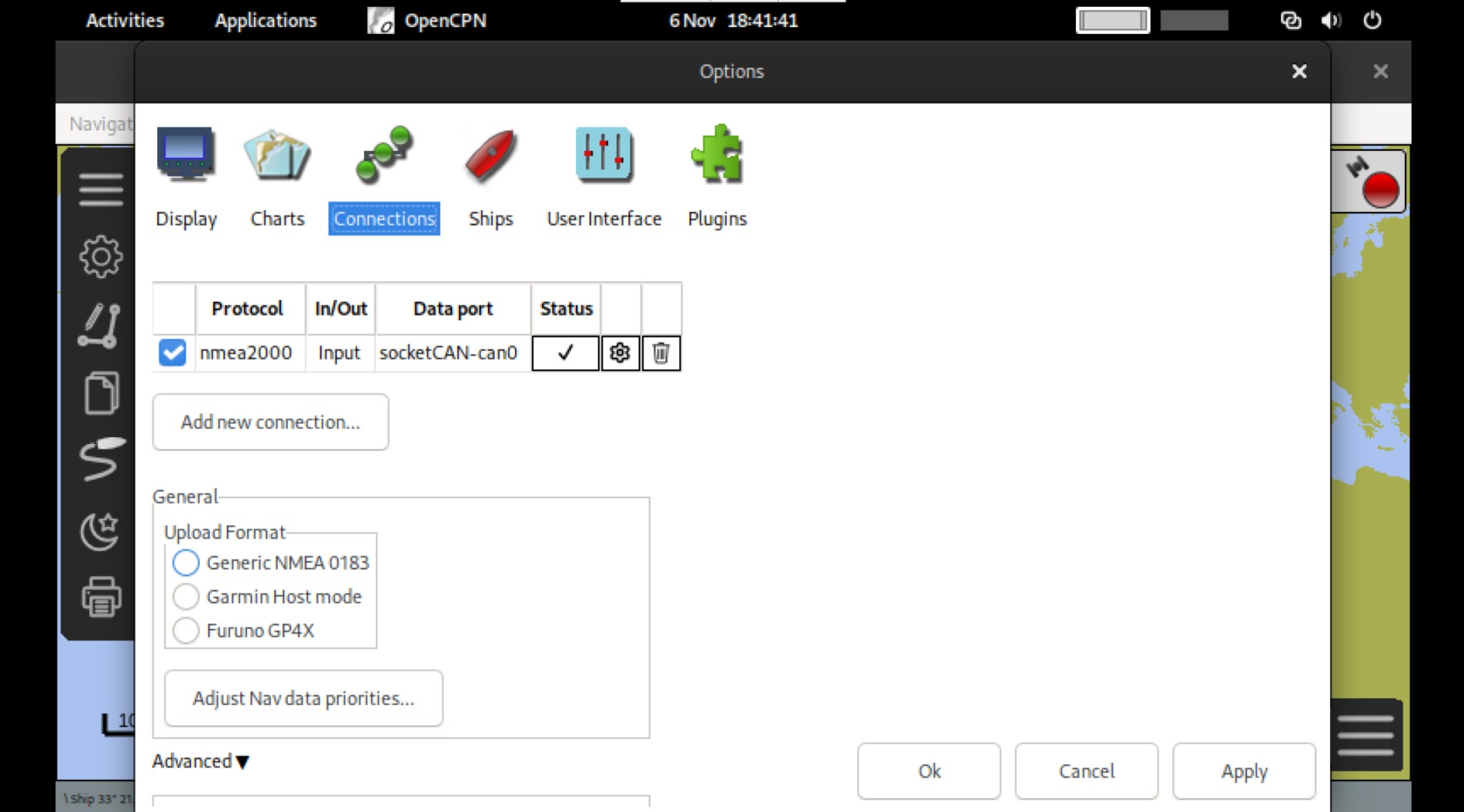
Connecting to NMEA 2000 via CAN on a Rockit Server Model 3
OpenCPN → Options ⚙ → Connections → Add Connection:
- Type: CAN (SocketCAN)
- Interface: can0
- Tick Input
can0 is exposed by the Rockit Server Model 3. No extra USB/serial gateway is required.
NMEA‑0183 over TCP/UDP on Rockit Server Model 1 or Model 3
OpenCPN → Options ⚙ → Connections → Add Connection:
- Type: Network
- Protocol: TCP (client)
- Address: Rockit Servers IP (e.g. 192.168.1.50)
- Port: 10110
- Tick Input
UDP alternative (if your multiplexer broadcasts):
- Type: Network → Protocol: UDP (listener) → Port: 2000
Step 6 — Plugins you’ll likely want
OpenCPN → Options ⚙ → Plugins → Catalog → Update
- o‑charts (vector charts; paid, simple licence model)
- AIS Radar (for an at‑a‑glance CPA/TPA view)
- GRIB / Weather Routing (if you plan to do passage work onboard)
- Climatology (historic seasonal overlays)
With Flatpak, plugins install into the OpenCPN sandbox. If a plugin doesn’t show, hit Update again and check architecture compatibility.
Step 7 — Remote access options (VNC)
VNC (RealVNC)
- Connect from RealVNC Viewer to your Rockit Servers IP address.
- For best performance over Wi‑Fi, drop colour depth to 16‑bit and turn on adaptive quality.
More Technical – Run OpenCPN headless on a virtual display
If you want OpenCPN rendering without a logged‑in desktop (e.g., to project via a browser stream or grab screenshots), you can use xvfb-run:
sudo apt install -y xvfb xvfb-run -a flatpak run org.opencpn.OpenCPN
Headless OpenCPN is great for always‑on AIS/GPS feeds. For interactive chartwork, use VNC instead.
Step 8 — Chart Management and GPS Connectivity
Download charts from your chosen provider (e.g., o‑charts) to a local folder (e.g., ~/Charts) and Add Directory in OpenCPN. Use o‑charts for curated vector sets; for raster/legacy BSB, ensure formats are supported by your build. After updates, hit Options → Charts → Force Full Database Rebuild.
Wi‑Fi GPS Data Source
If OpenCPN can’t read N2K directly you can still drive the chart with Wi‑Fi GPS. Many onboard multiplexers and mobile apps can broadcast NMEA‑0183 over the network.
Ensure your Rockit Server running OpenCPN is on the same Wi‑Fi network as the GPS source. If using a phone app, keep the app awake so it continues broadcasting.
Troubleshooting
No GPS/AIS data ? Double‑check the connection type and port. Watch the NMEA Debug window in OpenCPN for live sentences.
Plugins empty? With Flatpak, open the Plugins Catalog and click Update. Verify you’re on ARM64 builds for Pi OS 64‑bit.
Slow map panning? Close other 3D apps, or reduce chart quilting.
That’s it
You’ve now got OpenCPN running on your Rockit Server, pulling live data from NMEA and accessible from Laptop/Tablet via VNC.
As all Rockit Servers are custom build we are happy to add the additional software, if you want this pre‑loaded as part of a Rockit Server image build, drop us a note when you order and we will bundle it in.
Follow the links below to find out more about Rockit Server Devices and OpenCPN software.
Rockit Server Model 3 Standard
Rockit Server Model 1 Standard